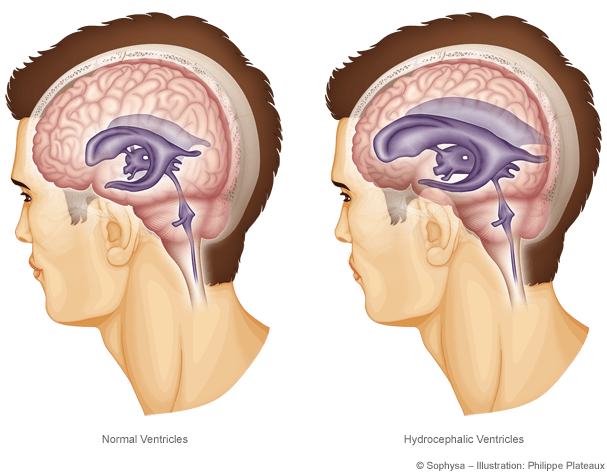
Hydrocephalus
Causes
- bleeding inside the brain – for example, if blood leaks over the surface of the brain (subarachnoid haemorrhage)
- blood clots in the brain (venous thrombosis)
- meningitis – an infection of the membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord.
- brain tumours.
- head injury.
Symptoms
- Headache.
- Blurred or double vision.
- Abnormal eye movements.
- Abnormal enlargement of a toddler’s head.
- Sleepiness or sluggishness.
- Nausea or vomiting.
- Unstable balance.
- Poor coordination.
Treatment
The most common treatment for hydrocephalus is the surgical insertion of a drainage system, called a shunt. It consists of a long, flexible tube with a valve that keeps fluid from the brain flowing in the right direction and at the proper rate.
Diagnosis
How is hydrocephalus diagnosed? Hydrocephalus is diagnosed through a neurological evaluation. Your healthcare provider may use brain imaging techniques such as ultrasounds, computer tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Other tests are often performed in adults to diagnose the condition.