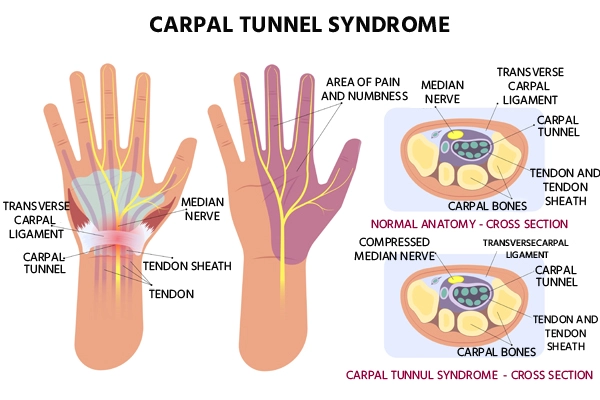
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Causes
Most cases of carpal tunnel syndrome have no specific cause, although any or all of the following may be a contributing factor: Frequent, repetitive, small movements with the hands (such as with typing or using a keyboard)
Symptoms
- Weakness when gripping objects with one or both hands.
- Pain or numbness in one or both hands.
- “Pins and needles” feeling in the fingers.
- Swollen feeling in the fingers.
- Burning or tingling in the fingers, especially the thumb and the index and middle fingers.
Treatment
Nonsurgical Treatment
Surgical Treatment
Surgical Procedure
Diagnosis
-
History of symptoms. Your provider will review the pattern of the symptoms. For example, because the median nerve doesn’t provide sensation to the little finger, symptoms in that finger may indicate a problem other than carpal tunnel syndrome.
Carpal tunnel syndrome symptoms usually occur while holding a phone or a newspaper or gripping a steering wheel. They also tend to occur at night and may wake you during the night, or you may notice the numbness when you wake up in the morning.
-
Physical examination. Your provider will conduct a physical examination. He or she will test the feeling in the fingers and the strength of the muscles in the hand.
Bending the wrist, tapping on the nerve or simply pressing on the nerve can trigger symptoms in many people.
- X-ray. Some providers recommend an X-ray of the affected wrist to exclude other causes of wrist pain, such as arthritis or a fracture. However, X-rays are not helpful in making a diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome.
- Ultrasound. Your provider may recommend an ultrasound of your wrist to get a good picture of the bones and nerve. This can help determine whether the nerve is being compressed.
- Electromyography. This test measures the tiny electrical discharges produced in muscles. During this test, your provider inserts a thin-needle electrode into specific muscles to evaluate the electrical activity when muscles contract and rest. This test can identify damage to the muscles controlled by the median nerve, and also may rule out other conditions.
- Nerve conduction study. In a variation of electromyography, two electrodes are taped to the skin. A small shock is passed through the median nerve to see if electrical impulses are slowed in the carpal tunnel. This test may be used to diagnose the condition and rule out other conditions.