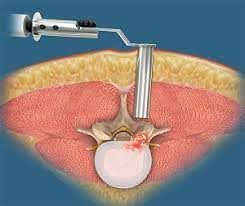
Microscopic Spinal Surgery
Causes
Indications for Microscopic Spine Surgery
- Spinal stenosis.
- Sciatic nerve pain.
- Spondylosis.
- Spondylolisthesis.
- Nerve damage.
- Scoliosis.
- Kyphosis.
- Degenerative disc disease.
Symptoms
Microscopic spine surgery is a relatively safe procedure; however, as with any surgery, some risks and complications may occur, such as:
- Infection.
- Blood loss.
- Blood clots or deep vein thrombosis.
- Anesthetic/allergic reactions.
- Neurovascular injury.
- Persistent pain.
- Bowel or bladder problems.
Treatment
Microdiscectomy is a very common, if not the most common, surgery performed by spine surgeons. The operation consists of removing a portion of the intervertebral disc, the herniated or protruding portion that is compressing the traversing spinal nerve root.
Diagnosis
Indications for Microscopic Spine SurgeryMicroscopic spine surgery can be indicated to treat several spinal conditions such as: Spinal stenosis. Sciatic nerve pain. Spondylosis.